
Dr. Nicola Normanno, Director, Translational Research, National Cancer Institute, Italy - Pascale Foundation
In this webinar, Dr. Nicola Normanno presents a research study of the analytical validation for the in-house assessment of HRD with the Oncomine Comprehensive Assay Plus on a cohort of ovarian cancer samples, including how the genomic instability metric (GIM) compares to orthogonal methods, and a retrospective analysis of clinical outcomes from the same cohort.
In this webinar, Dr. Nicola Normanno provides an overview of methods for assessing HRD, and his experience evaluating the Oncomine Comprehensive Assay Plus, a targeted NGS approach that can help clinical research in identifying all relevant biomarkers, including HRD.
Minimize the resources and expertise required to generate CGP results by combining a highly automated workflow with a complete bioinformatics pipeline all from a single supplier.
All relevant single gene and complex biomarkers including homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) based on genomic instability metric (GIM), tumor mutational burden (TMB) and microsatellite instability (MSI).
Low FFPE sample input of 20 ng DNA and RNA means more, and smaller, samples can be tested
Empower lab efficiency by reducing hands on time and possible errors due to handling. The highly automated workflow with Ion Torrent Chef and Ion Torrent GeneStudio S5 with dedicated bioinformatics pipelines including Oncomine Reporter means ~1 hour of hands-on time.
Single-gene biomarkers—Broad range of single-gene variants, such as single-nucleotide variants (SNVs), insertions and deletions (indels), novel and known fusions, splice variants, and copy number variants (CNVs), including both copy number gains and losses
Multiple-gene biomarkers—Tumor mutational burden (TMB), predisposition to genetic hypermutability by comparing microsatellite instability (MSI) regions, and analyze mutational signatures for insights into etiological factors in tumorigenesis
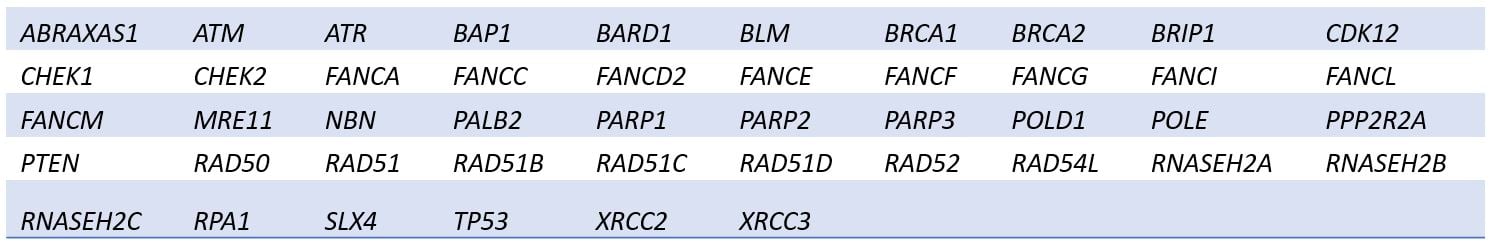
Homologous recombination deficiency— Assess causes and consequences HRD including mutations in 42 key genes in the homologous recombination repair (HRR) pathway as well as genomic scarring by the GIM.
Read Article: A Comprehensive Answer for Cancer: Is Comprehensive Genomic Profiling Always the Right Approach?
A multi-center study reported that more than half of all samples would not be suitable for hybrid capture-based NGS, while 93.8% of samples below 25mm2 were successfully tested by amplicon-based NGS methods.
Homologous recombination deficiency is becoming an important new biomarker in precision oncology clinical research.Under normal conditions, genes in the HRR pathway repair DNA damage. Errors in the HRR pathway, such as loss-of-function or deleterious mutations in the associated genes, can lead to higher levels of genomic instability - the HRD phenotype. HRD has been shown to be relevant in certain tumors, such as ovarian and prostate cancers, and is being extensively studied in clinical research.
HRD can be assessed using two main strategies:
The significant role of HRR genes in maintaining genome stability and tumor suppression has been studied extensively,
especially in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. In recent years, it has been demonstrated that alterations in other homologous recombination repair pathway genes may lead to genomic instability and cancer cell development. The status of HRR genes are now considered an important biomarkers for precision oncology research.
The Oncomine Comprehensive Assay Plus measures genomic scarring with the genomic instability metric (GIM). GIM is a numeric value between 0 and 100 that summarizes unbalanced copy number changes using genomic segmentation.
Figure B demonstrates sample-level LOH compared with Applied Biosystems(TM) OncoScan(TM) CNV Assay and Figure C shows a comparison of GIM for BRCA-positive and BRCA-negative ovarian cancer samples (n = 46). No: no pathogenic BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation present. Yes: pathogenic BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation present. Source: internal R&D data.
No, one size does not fit all. For example, let’s take non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) samples. All biomarkers relevant for clinical research can be tested by one, 50 gene targeted panel. It’s cheaper, faster, and it requires less sample input, which is critical in NSCLC, where “tissue is still an issue”. There are four key scenarios in which comprehensive genomic profiling
would be most impactful.
Learn about them in The Pathologist Article “A Comprehensive Answer for Cancer”.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
We've detected your location to be Japan.
Sorry, you cannot access this website. The content on www.oncomine.com is only intended for healthcare professionals. Formore information on our research solutions, please visit ThermoFisher.com
このウェブサイトは、日本国内の医療関係者の方への情報提供を目的としており、一般の方に対する情報提供を目的としたものではないことをご了承ください。研究用製品の情報はThermoFisher.comよりご覧ください。